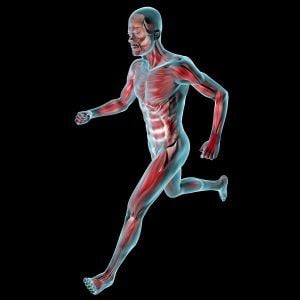
How well do you know the muscles in the body?
There are 640 muscles in the human body. Can you name the longest, strongest, and biggest muscles?
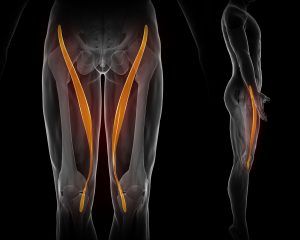
What is the Longest Muscle?
The answer is the sartorius muscle. The sartorius is a superficial muscle that runs the entire length of the thigh and plays a role in flexing the knee and hip.
The satoris muscle is involved in a wide range of lower-body actions so finding ways to strengthen it is relatively simple. You could for a walk or a jog or do squats or a lunges. Other workouts to try would be lateral step ups, lateral band walks or plie squats.
What is the Biggest Muscle?
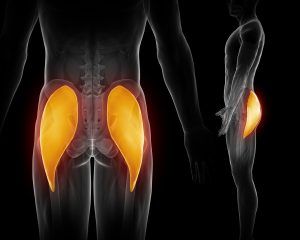
The gluteus maximus. The gluteus maximus is responsible for stabilizing the hip joint and plays a big role in our ability to move our thighs. With a name like gluetus MAXimus it shouldn't be hard to remember it's the biggest muscle in the body.
In addition to the gluteus maximus the your glutes include two other muscles as well, the gluteus medius and the gluteus minimus.
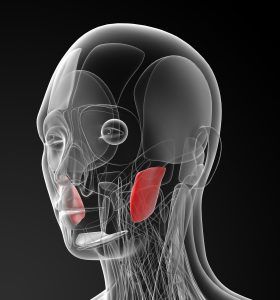
What is the strongest muscle in the body?
This one is a little more controversial because there are a few different ways to measure strength. The most commonly accepted answer is the masseter muscle. This tiny but strong muscle allows us to forcefully close our jaws.
The masseter muscle is one of the strongest and also many times one of the tightest muscles. If your jaw is tense massaging your masseter muscles may help reduce discomfort.
Now that you know the longest, strongest and biggest muscles in the body you are ready to take on Jeopardy. Muscles for 500 Alex.
Want more info? Follow us on Facebook for all of the latest health and fitness news.
Topics: LivRite News
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disease in which the body’s inability to produce enough insulin causes levels of glucose in the blood to leave the normal range. The two most common forms of diabetes are Type I and Type II.
How many people suffer from it?
Diabetes has become so prevalent that according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) 29.1 million people living in the United States suffer from diabetes and another 86 million are considered pre diabetic. Nearly a third of all US adults are either diabetic or pre-diabetic.
What is insulin?
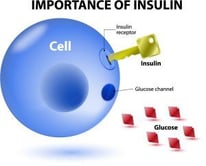
To be able to understand how diabetes affects the human body it is critical to look at insulin’s role in the process. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose as fuel for energy. This hormone is made in the pancreas by beta cells. If the body cannot make enough insulin to keep blood glucose levels normal then Doctors often prescribe insulin to be administered either by injection or through an insulin pump.
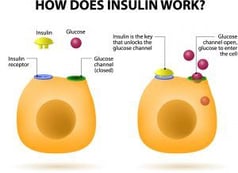
Insulin acts as a key to open up the door that allows glucose to come into the cell where it is broken down and can then be used as energy by the cells. If there is no insulin or not enough insulin then the “door” that lets glucose into the cell remains locked and the glucose can’t get through and therefore remains in the blood stream.
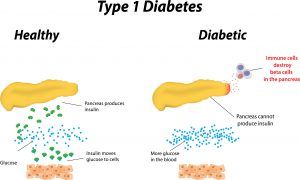
What is type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is predominantly diagnosed in children and young adults. Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the body’s inability to break down sugars and starches into glucose. For people suffering from type 1 diabetes, their immune cells destroy beta cells in the pancreas that are normally in charge of creating insulin. Since the pancreas can’t create the insulin that would normally allow glucose to enter the cells, the glucose begins to accumulate in the bloodstream which can lead to hyperglycemia. Through the aide of various insulin therapies people suffering from type 1 diabetes can learn to manage their disease.
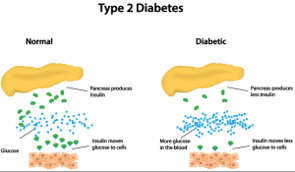
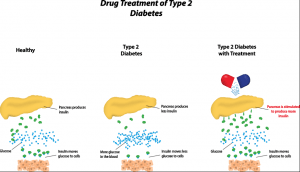
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by the body’s inability to use insulin properly (insulin resistance). To compensate for this the pancreas will try to make more insulin but it won’t be able to keep up and therefore glucose accumulates in the bloodstream.
If the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to keep blood glucose levels in the normal range then Doctors often prescribe insulin medication
Benefits of Exercise for Diabetics
Type 1
According to the American Council On Exercise (ACE) type 1 diabetics can reduce their risk of coronary artery disease, improve insulin-receptor sensitivity, and improve functional capacity with a program of regular physical activity.
Type 2
The benefits of exercise for type 2 diabetics are vast. According to ACE these benefits include but are not limited to prevention of coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. Regular exercise can also help reduce elevated bodyweight and improve lipid profiles in type 2 diabetics. Oftentimes weight loss through appropriate diet and exercise can lead to, under a medical professional’s supervision, a reduction in the amount of insulin medication needed.
Type 1 Diabetes Recommended Exercise
Type 1 diabetics are encouraged to exercise at least 3 times a weeks and exercise should be supplemented with a consistent pattern of diet and insulin dosage. This consistency helps ensure glucose control.
It is recommend that type 1 diabetics gradually build up to 30 minutes or more per session. Long duration activities and high intensity activities should be avoided because long duration exercises can increase the risk of hypoglycemia and high intensity exercises can increase the risk of hyperglycemia. Weight lifting is recommended for type 1 diabetics without complications.
Type 2 Diabetes Recommended Exercise
According to the International Sports Science Association (ISSA), Type 2 diabetics are advised to exercise at a low intensity level and for a longer duration. Generally speaking, aerobic exercises should be performed at least 5 times a week for 40-60 minutes per workout. Low to moderate intensity resistance training is also recommended twice a week. According to ACE, a training program consisting of a combination of aerobic and resistance training can produce the best results for type 2 diabetics.
Some Exercise Precautions for Diabetics
- Diabetic individuals should undergo a complete medical evaluation for beginning an exercise program
- Monitor blood glucose levels before and after exercise
- Eat additional carbohydrates as necessary before exercising to avoid hypoglycemia
- Have carb based foods readily available during exercise
- Avoid exercise during peak insulin activity
- Try to exercise with a partner or a personal trainer
- Stay hydrated! Dehydration can impact blood glucose levels
If you would like to know more about diabetes, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has some fantastic information.
Like the Motivator?
Be sure to like us on Facebook and follow us on twitter for the latest in club news
Topics: LivRite News